Market trends are not in favour of Telecom Service /providers with increasing use of OTT ( Over The Top ) applications like WhatsApp, Facebook messenger, Google hangouts, skype, Viber, etc. OTT applications are often blamed to take a stake in voice traffic revenue by using IP calls where the telco could’ve charged based on its rate plan of call seconds. This especially intensifies for long-distance or international calls where customers can use OTT providers instead of expensive telco rate plans.
What is an OTT ?
An Over The Top ( OTT ) application is one which provides communication services over Internet . Therefore these bypass the communication billing system setup by a Telecom Operator , resulting in no gain or loss of revenue to Telecom Operator who is providing the Internet service to user in first place .
Hence we see that OTT are major source of concern for Telecom Operators whose traditional and obviously expensive ( when compared to OTTs free service ) billing models are facing disruption .
Telecom Regulatory bodies around the world
The telecom regulatory authorities in some of the countries are for example listed as :
- Afghanistan Telecom Regulatory Authority (ATRA) – Afganistan
- Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA) – Australia
- Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission (BTRC) – Bnagaladesh
- Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) – Canada
- Ministry of Information Industry (MII) – China
- Autorité de Régulation des Communications Électroniques et des Postes (ARCEP) – France
- Bundesnetzagentur (BNA) – Germany
- Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) – India
- Ministry for Communications and Informatization of the Russian Federation (Minsvyaz) – Russia
- Infocomm Development Authority of Singapore (IDA) – Singapore
- Independent Communications Authority of South Africa (ICASA) – south Africa
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC) , National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners (regulators of individual states) (NARUC) , CTIA – The Wireless Association (CTIA) – USA
Such telecom regulatory bodies get to decide whether to enforce differential price to end consumers for using OTT so that telecom service providers can benefit or keep the Internet fair and open by passing Net Neutrality Laws and Bills and amendments .
What is Net Neaurality ?
The fundamental principle of Net Neurality is that Telecom Operators should not block , slow down or charge consumers extra for using other services as their means of communication. This states that it is wrong to charge users above the regular data rates for using VOIP apps and other internet based communication services.
The following counteries have adopted principles of Net Neutrality by passing bills or making law .
- Chile – Chile’s General Law of Telecommunications, “No [ISP] can block, interfere with, discriminate, hinder, nor restrict the right of any Internet user of using, send, receive, or offer any content, application, or legitimate service through the Internet, as well as any activity or legitimate use conducted through the Internet.”
- Brazil – ” Internet Bill of Rights ” makes equal access to internet mandatory in Brazil .
- Netherlands – Even European Union has adopted Netherlands’ Net Neutrality amendment which reads “traffic should be treated equally, without discrimination, restriction or interference, independent of the sender, receiver, type, content, device, service or application.”
- USA – Citizens make ‘We the People’ platform to ‘Restore Net Neutrality By Directing the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to Classify Internet Providers as ‘Common Carriers‘. Therefore not allowing them to either throttle speed by paid prioritization , discriminate in pricing or block any broadband access to legal content . Above facts are from this tech.firstpost.com article.
Inspite of the fact that I Support Net Neutrality with all my heart , as a telecom engineer I understand the cost investment made by Telecom operators in providing am efficient communication network to its subscribers ( Access , Network and Application layers ). Therefor I do have my sympathies with the Telcos and to level out the wide ranging conflict between Telcos and ISP ( Internet Service Providers ) , I pen down the following points which reflect the Telecom Operators Problems and also highlight the solutions that can be adopted to counteract the OTT threat .
Depleting revenue for Telco
- Messaging – OTT messaging cost operators $13.9 billion, or 9% of message revenue in 2013
- Voice – Voice services under threat from VOIP services like Skype, Viber
- OTT apps – Voice & Message apps have been the operator’s biggest headache. Its time Operator should launch its own OTT Services
- Data Traffic – The utilization is yet to reach its peak. Will face challenges from WiFi access
- Critical Pain areas – Erosion of Operator’s revenue from voice and (especially) messaging
Telco’s OTT Application
At this stage, a telecom Service provider / Operator must enter the apps market and bring forth a Messenger which is more powerful, interactive and awesome than an OTT application. Fortunately, the Operator can always couple this application with his background telecom infrastructure to provide the edge in performance and functionalities.
Road block while developing a OTT application for a Telecom Service Provider :
- Investment in Data Network is not being utilized due to lack of service
- Reuse of Existing business Logic and extending the service reach across devices and networks is tough
- Operator already has full fledged network Infrastructure in Place
- Desire for minimum CAPEX while investing in new technologies
- compete with OTT players and open new revenue streams is a challenge
Next we find the way of solving the problems and integrating them together to form a Solution .
OTT Application for Telecom Service provider
- Introduce new services to benefit from investment on Data Plans and Bandwidth
- Expose REST API to enable 3trd party Integration with existing network Infrastructure
- Partner with individual OTT players to make new services that do not compete on core competencies like billing etc
- Use protocols like SIP that reduce CAPEX and have goto market more quickly
- Go for enriched service that lead to better user experience
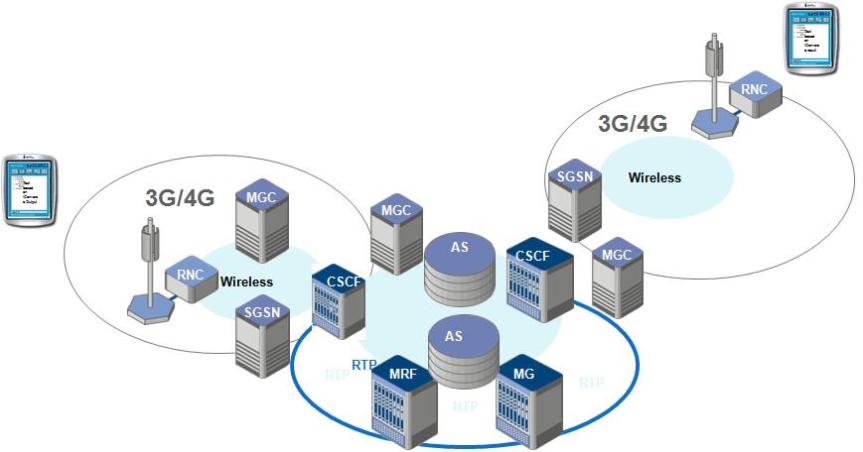
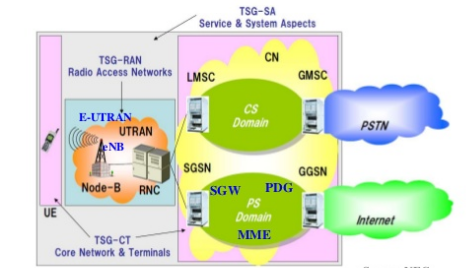
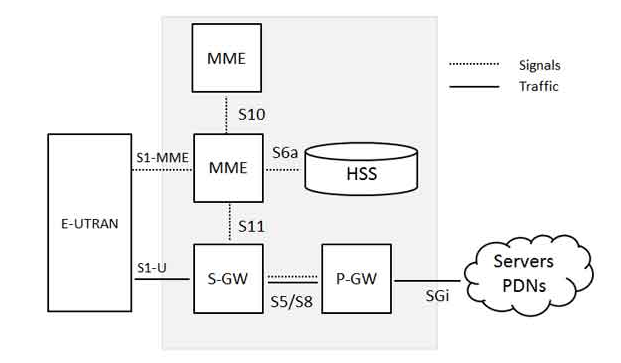
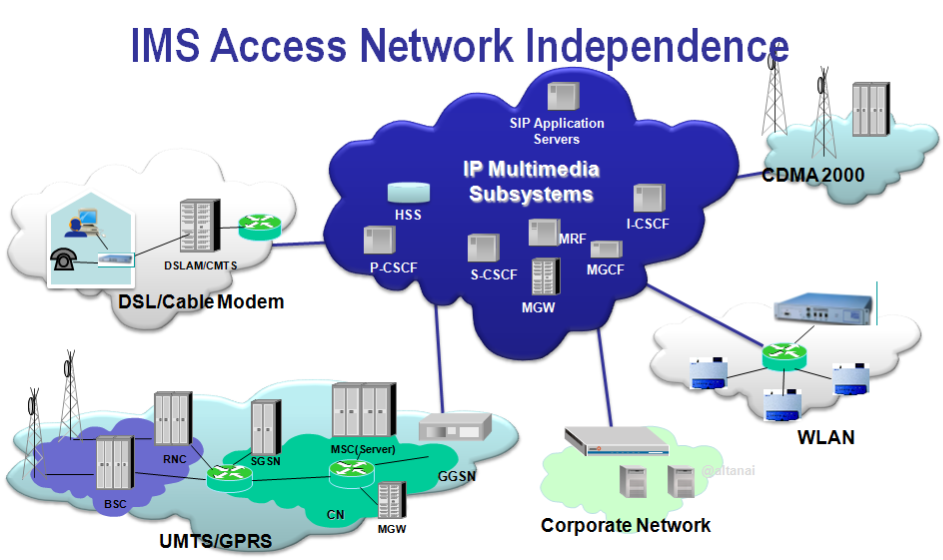
This write-up outlines the process of creating an OTT application for a Telecom Service Provider. Components for the application include cloud Address Book, Video Chatting, Location share, Contact synchronization ,REST-based thin client , OS and device agnostic etc shown in the figure below:

The Application is designed to close knit with Operator’s own infrastructure hence the crucial entities like Network Address Book , Location Service are synced and fetched from Backend Network .
OTT application Feature Overview
Smart Address Book
- Automatic: Get contacts from Gmail, Facebook
- Fast search by first, last name, frequently
- dialed number
- Roadmap: View calendar events
- Personal: Get image from Gmail and display in contacts list
Geo Location
- Share own location during chatting
- Get map for calculating the distance between two chat users
- Roadmap : Trigger device (say Switch on/off AC before reaching home) from a threshold distance away from home location
Messaging
- Ad-hoc Chat
- Session Based Chat
- Voice Input for texting
- Presence information of contacts
- RoadMap: Legacy message integration
Telephony
- Voice call to mobile
- Voice call to PSTN
- Video call to other @imAll user
- Share images during voice call to other
Device agnostic
- Compatible with IOS, windows
- Can run as native app on ipad
- Can run as browser client on windows
- RoadMap: native app for android, windows phone,blackberry10
Roadmap

- To upgrade the application and provide enganced and enrich service support the I propose the following roadmap.
- From plain vanilla voice and video calling ( supported by every other OTT application ) our application should progress towards legacy telecom support whihc included PSTN , GSM , ISDN etc . This requires backbone of telecom network and a good setup for media codec conversion to suit various legacy media codecs .
Road Map from Traditional to New age services
- Voice and video calling
- Legacy services support like MMS and SMS
- Integration with 3rd party Vendors
- Give new enriched services like Multilingual support , file transfer , screen-sharing etc
- give facility to integrated web plugins for web calling
To keep the interest of customers it is essential that the application be supported on other popular OTT services like skype , Gtalk . for exmaple a caller should be able to make call from Skype / Gtalk to our application .Multilingual capabilities, support for larger protocol spectrum will just act like icing on the cake .
How does it benefit the Operator??
- Saves on development cost and time
- Device Agnostic OTT Applications
- Simplified Service deployment
- Saves licensing cost per client
- Reuses existing Messaging and Address Book service logic.
- Open New Revenue Streams for operator
- No separate SIP stack required for the client
- Faster Time to Market
Update : At the time of writing this post I did not anticipate the wave of change that bring focus on subjects like “net neutrality” , ” Save the internet” and “free internet”. However now most of the telcos providers have either joined the bandwagon by prividing SIP trunk endpoinst for cloud teelphony providers ( eg twilio, Google Calls) or have made their own IP call application for B2B customers.