- B2BUA
- Features
- Security
- Topology hiding
- Connectivity
- Least Cost Routing based on MoS
- Protocol translations
- Automatic Rerouting
- QoS
- Regulatory
- Media services
- NAT
- Statistics and billing information
- Security
- Gateways vs SBC
- Building a SBC
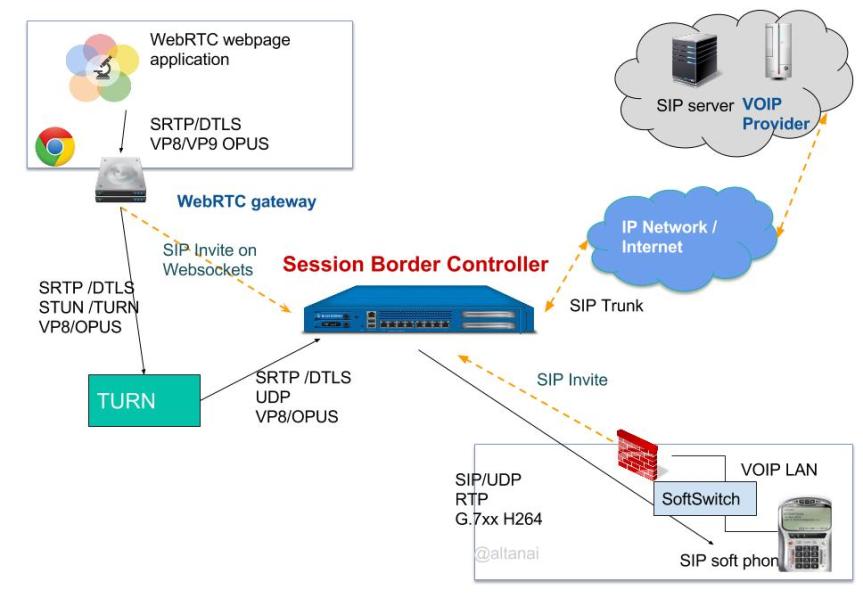
Unified communication services build around WebRTC should be vendor agnostic and multi-tenant and be supported by other Communication Service Providers (CSPs), SIP trunks, PBXs, Telecom Equipment Manufacturers (TEMs), and Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS). This can happen if all endpoints adhere to SIP standards in most updated RFC. However since not all are on the boat , Session border controllers are a great way to mitigate the differences and provide seamless connectivity to signalling and media , which could be between WebRTC, SIP or PSTN, from TDM to IP .
Session Border Controllers ( SBC ) assist in controlling the signalling and usually also the media streams involved in calls and sessions. They are often part of a VOIP network on the border where there are 2 peer networks of service providers such as backbone network and access network of corporate communication system which is behind firewall.
A more complex example is that of a large corporation where different departments have security needs for each location and perhaps for each kind of data. In this case, filtering routers or other network elements are used to control the flow of data streams. It is the job of a session border controller to assist policy administrators in managing the flow of session data across these borders.
– wikipedia
SBC act like a SIP-aware firewall with proxy/B2BUA.
What is B2BUA?
A Back to back user agent ( B2BUA ) is a proxy-like server that splits a SIP transaction in two pieces:
- on the side facing User Agent Client (UAC), it acts as server;
- on the side facing User Agent Server (UAS) it acts as a client.
SBC mostly have public url address for teleworkers and a internal IP for enterprise/ inner LAN . This enables users connected to enterprise LAN ( who do not have public address ) to make a call to user outside of their network. During this process SBC takes care of following while relaying packets .
- Security
- Connectivity
- Qos
- Regulatory
- Media Services
- Statistics and billing information
Explaining the functions of SBC in detail
1. Security
SBCs provide security features such as encryption, authentication, and firewall capabilities to protect the network from unauthorized access and attacks. SBCs are often used by corporations along with firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to enable VoIP calls to and from a protected enterprise network. VoIP service providers use SBCs to allow the use of VoIP protocols from private networks with Internet connections using NAT, and also to implement strong security measures that are necessary to maintain a high quality of service. The security features includes :
- Prevent malicious attacks on network such as DOS, DDos.
- Intrusion detection
- cryptographic authentication
- Identity/URL based access control
- Blacklisting bad endpoints
- Malformed packet protection
- Encryption of signaling (via TLS and IPSec) and media (SRTP)
- Stateful signalling and Validation
- Toll Fraud – detect who is intending to use the telecom services without paying up
Topology hiding
SBC hides and anonymize secure information like IP ports before forwarding message to outside world . This helps protect the internal node of Operators such as PSTN gateways or SIP proxies from revealing outside.
2. Connectivity
As SBC offers IP-to-IP network boundary, it recives SIP request from users like REGISTER , INVITE and routes them towards destination, making their IP. During this process it performs various operations like
- NAT traversal
- IPv4 to IPv6 inter-working
- VPN connectivity
- SIP normalization via SIP message and header manipulation
- Multi vendor protocol normalization
Further Routing features includes :
Least Cost Routing based on MoS ( Mean Opinion Score ) : Choosing a path based on MoS is better than chooisng any random path .
Protocol translations SBCs can bridge WebRTC calls with other communication protocols such as SIP, H.323, and PSTN to enable communication between different systems and networks.
In essence SBC achieve interoperability, overcoming some of the problems that firewalls and network address translators (NATs) present for VoIP calls.
Automatic Rerouting
Connectivity loss from UA for whole branch is detected by timeouts . But they can also be detected by audio trough SIP OPTIONS by SBC . In such connectivity loss , SBC decides rerouting or sending back 504 to caller .

4. QoS
To introduce performance optimization and business rules in call management QoS is very important. This includes the following:
- Traffic policing
- Resource allocation
- Rate limiting
- Call Admission Control (CAC)
- ToS/DSCP bit setting
- Recording and Audit of messages , voice calls , files
System and event logging
SBCs can log call information and statistics, and provide real-time monitoring capabilities to troubleshoot and diagnose issues with WebRTC calls.
5. Regulatory
Govt policies ( such as ambulance , police ) and/ or enterprise policies may require some calls to be holding priority over others . This can also be configured under SBC as emergency calls and prioritization.
Some instances may require communication provider to comply with lawful bodies and provide session information or content , this is also called as Lawful interception (LI) . This enables security officials to collect specific information rather than examining all the traffic that passes through a particular router. This is also part of SBC.
6. Media services
Many of the new generation of SBCs also provide built-in digital signal processors (DSPs) to enable them to offer border-based media control and services such as- DTMF relay , Media transcoding , Tones and announcements etc.
WebRTC enabled SBC’s also provide conversion between DTLS-SRTP, to and from RTCP/RTP. Also transcoding for Opus into G7xx codecs and ability to relay VP8/VP9 and H.264 codecs.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
SBCs can handle Network Address Translation (NAT) to allow WebRTC clients behind a NAT to connect to other clients outside of the NAT.
7. Statistics and billing information
SBC have an interface with and OSS/BSS systems for billing process , as almost all traffic that pass through the edge of the network passes via SBC. For this reason it is also used to gather Statistics and usage-based information like bandwidth, memory and CPU. PCAP traces of both signaling and media information of specific sessions .
New feature rich SBCs also have built-in digital signal processors (DSPs). Thus able to provide more control over session’s media/voice. They also add services like Relay and Interworking, Media Transcoding, Tones and Announcements, DTMF etc.
SBCs act as a security gateway and traffic manager for WebRTC sessions, ensuring that the communication is secure, of good quality, and can traverse different networks and protocols.

Diagram Component Description
Gateways vs SBC
Gateways provide compression or decompression, control signaling, call routing, and packetizing.
PSTN Gateway : Converts analog to VOIP and vice versa . Only audio no support for rich multimedia .
VOIP Gateway : A VoIP Gateway acts like a translator converting digital telecom lines to VoIP . VOIP gateway often also include voice and fax. They also have interfaces to Soft switches and network management systems.
WebRTC Gateway : They help in providing NAT with ICE-lite and STUN connectivity for peers behind policies and Firewall .
SIP trunking : Enterprises save on significant operation cost by switching to IP /SIP trunking in place of TDM (Time Division Multiplexing). Read more on SIP trunk and VPN here.
SIP Server : A Telecom application server ( SIP Server ) is useful for building VAS ( Value Added Services ) and other fine grained policies on real time services . Read more on SIP Servers here .
VOIP/SIP service Provider : There are many Worldwide SIP Service providers such as Verizon in USA , BT in europe, Swisscom in Switzerland etc .
Building a SBC
The latest trends in Telecommunications industry demand an open standardized SBC to cater to growing and large array of SIP Trunking, Unified Multimedia Communications UC&C, VoLTE, VoWi-Fi, RCS and OTT services worldwide . Building an SBC requires that it meet the following prime requirements :
- software centric
- Cloud Deploybale
- Rich multimedia (audio , video , files etc) processing
- open interfaces
- The end product should be flexible to be deployed as COTS ( Commercial Off the shelf) product or as a virtual network function in the NFV cloud.
- Multi Configuration , should be supported such as Hosted or Cloud deployed .
- Overcome inconsistencies in SIP from different Vendors
- Security and Lawful Interception
- Carrier Grade Scaling
Flow Diagram

Thus we see how SBC became important part of comm systems developed over SIP and MGCP. SBC offer B2BUA ( Back to Back user agent) behavior to control both signalling and media traffic.