WebRTC is an evolving technology which promises simplified communication platform and stack for developers and hassslefree experience for users. It has the potential to provides in-context, call routed to the best personnel in service calls. Real time mapping of caller’s IP , locations and source metadata can be used for IVR eliminated. Such a complete collaboration tool is possible through WebRTC which is easy set-up, requires no installation no pugins and no download. Extremely secure, WebRTC can interoperate with existing VoIP, video conferencing and even PSTN. The only concern is the Integration with legacy PSTN and teleco environment.
In the present age of IP telephony when telecom convergence is the big thing all around the world, need of the hours is to enable fixed and mobile Service Providers ( SP ) to monetize the subscriber’s phone by extending it to new web based services. SPs can offer a WebRTC Communicator endpoint that uses the same phone number as the subscriber’s fixed or mobile phone. Advanced features enable calls to be transferred between fixed-line, mobile and WebRTC endpoints.

GSM is incompatible with WebRTC media stream due to legacy codecs, even if the WebRTC UA was to support these codecs the signalling translation will be a dffucult feat. Signalling is used for subscriber mobility, subscriber registration, call establishment, etc. Mobile Application Part (MAP), Base Station System Application part (BSSAP), Direct Transfer Application part (DTAP), ISDN User Part (ISUP) are some of the protocols making up GSM. In my opinion Some of the ways to integrate WebRTC to GSM backened could be
- Develop GSM-To-IP Interworking Component and integrate it with GSM network components (like BTS ).
- Integrate solution with H.323 based VoIP (Voice Over IP) components like Gatekeeper, Gateways/PBXs, to provide a complete voice/data network solution
Using telco service provider’s SIP trunk , if available, is the easiest way to conect to such backened communication systems.

- •A interface – connection between MSC and BSC;
- Abis interface – connection between BSC and BTS;
- D interface – connection between MSC and HLR;
- Um interface – radio connection between MS and BTS.
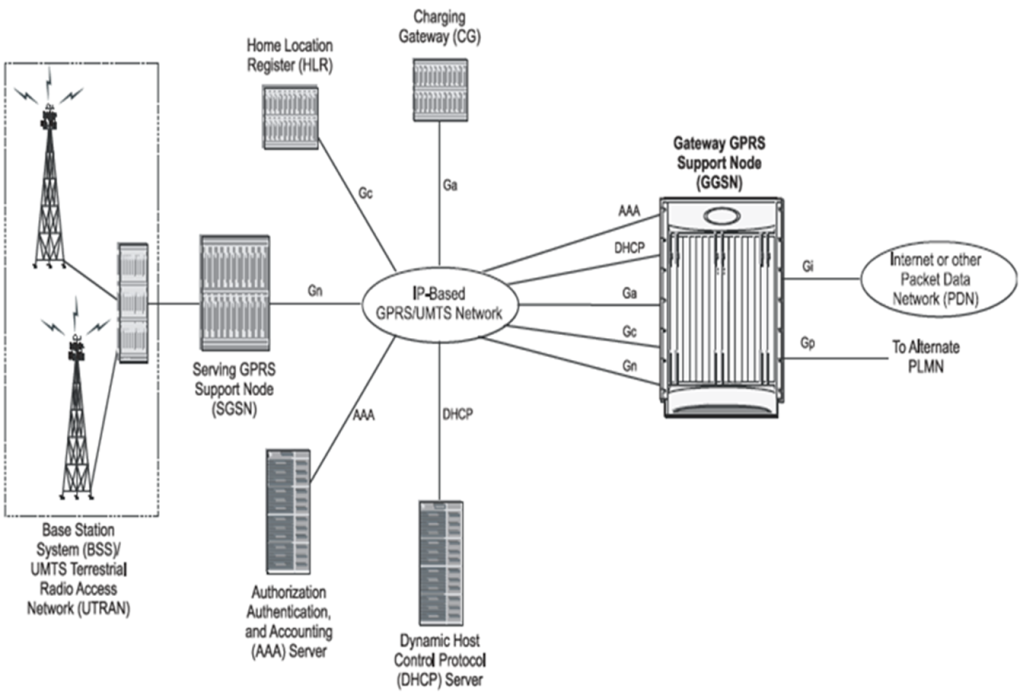
GPRS/UMTS Mobile Network can be compatible to WebRTC via Data based communication on GPRS gateway.
LTE Network using Evolves Packet Core can communicate with WebRTC using realtime transcoding and SIP (Session initiation protocol) endpoints conneted to core IMS. AnICE server provides the reflexive IP addresses that the WebRTC implementation needs; the signaling gateway converts the WebRTC webapp’s communication into SIP/IMS signaling and the media relay converts the WebRTC media framing into the telco conformant representation.

Interworking between a WebRTC enabled browser and IMS based Telco Backened : A session is established so that the web app sends an initial INVITE, including an SDP offer for the “outgoing” stream, to the gateway. The signalling gateway will reserve the resources from the media relay in both directions. Consequently, the signalling gateway will send an SDP answer to the initial INVITE and create an SDP offer of its own. This SDP offer is carried in a SIP UPDATE. Once the media between the web app and media relay is set, the session will progress towards IMS and will be handled like any other session. At this point, the media relay has mapped two unidirectional “web app streams” into one bidirectional “IMS stream” and will forward all media between the two. The mapping is done for both audio and video streams, meaning that we are able to support both audio and video calls between WebRTC and Telco clients and conferences.

WebRTC bypasses many limitation of earlier p2p (Peer-to-peer media) streaming frameworks like NATS. It opens avenues for innovative cross-platform use cases such as Healthcare, service technicians on call, Retail and financial communications, phone payments and insurance claims. Other applications such as Unified communication and collaboration are applicable for sales, CRM, remote education etc.


SPs can offer 3rd Party WebRTC endpoints to access the user’s phone number and subscription . E.g. enable web applications such as Facebook, Amazon or Netflix to allow their users to make/receive calls or messages directly from the web applications
Revenue Streams :
- monthly fee for access to WebRTC endpoints and for receiving calls from by 3rd Party WebRTC endpoints
- One time upgrade fees for Accessing the Web service integration with telecom network like a plan upgrade
Brownie points
- No software is required to be downloaded on the subscriber’s computer, tablet or mobile phone
- No desktop support required for the service provider
Plans For Consumer Customers:
- Subscribers can use the WebRTC endpoints on their computers, tablets or mobile phones as a fixed-line device at home, as a desktop solution when away from home and to avoid international tolls when traveling
- Subscribers can connect their web services (e.g. Websites , Facebook, Amazon, Netflix) to their fixed or mobile services subscriptions using their SP-provided phone number
Plans For SP Enterprise Customers:
- Enterprises can deploy a WebRTC endpoint for their employees that provides a single corporate communications endpoint that can be connected to any of the corporation’s UC/PBX and Call Recording systems
- Employees can use the WebRTC endpoint as their office phone at work, home or when traveling
- Connects to all leading UC/PBX and Recording platforms simultaneously
- Enterprises can deploy a single WebRTC endpoint across all their UC/PBX and Recording platforms – current and future
- Easy for IT departments to deploy – no software is required to be downloaded to employees’ computers, tablets or mobile phones
- Enables corporate policies and features from the WebRTC endpoint including
- Displaying the corporate identity
- Routing calls via corporate networks
- Tracking and Recording calls and messages




