XMPP is a open XML technology for real-time communication. Applications are instant messaging, presence, media negotiation, whiteboarding, collaboration, lightweight middleware, content syndication, and generalized XML routing according to XMPP standards Foundation (XSF) .
Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) is a communications protocol for message-oriented middleware based on XML (Extensible Markup Language). – wikipedia
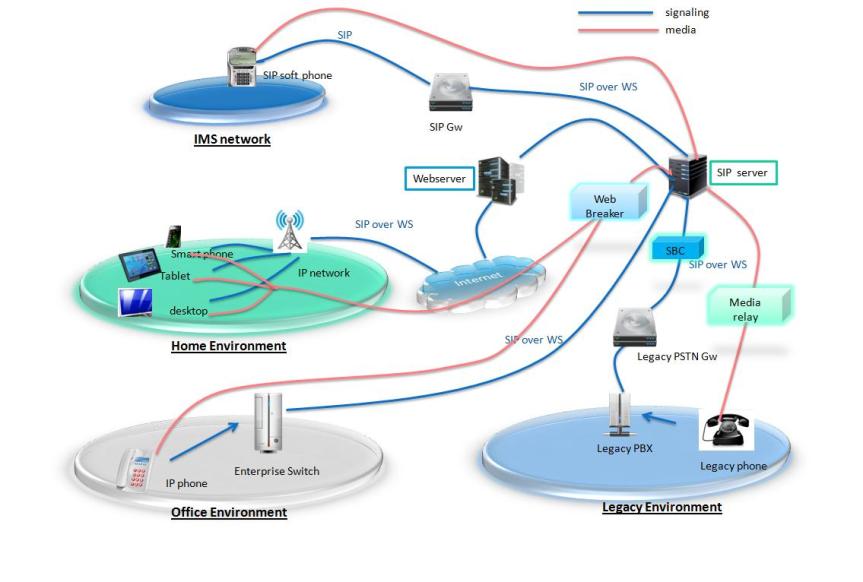
XMPP Server
Some popular servers on XMPP are ejabbred ( written in erlang licensed by GPL2) and openfire ( written in Java licensed by Apache ). This article will show the installation steps for openfire on Ubuntu version 15 64 bit system
1.Install the tar from http://www.igniterealtime.org/downloads/index.jsp

2. Extract and move the folder to /opt
3. Goto bin and run openfire server with ./openfire start

4. Gotot the web admin url http://localhost:9090/ . For first time the setup screen will appear

5. Proceed with installation .

It will show screens to select the mysql driver and database . Create a empty db name called openfiredb and add that to mysql url in setup screen of openfire
It will also request a administrator username and password I choose to give admin admin as the username and password alike .
6. change the interface inside of openfire.xml file in location /opt/openfire/conf
<network>
<interface>127.0.0.1</interface>
</network>
we can also review the mysql connection string
<database>
<defaultProvider>
<driver>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driver>
<serverURL>jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/openfiredb?rewriteBatchedStatements=true</serverURL>
<username encrypted=”true”><<someval>></username>
<password encrypted=”true”> <<someval>></password>
<testSQL>select 1</testSQL>
<testBeforeUse>false</testBeforeUse>
<testAfterUse>false</testAfterUse>
<minConnections>5</minConnections>
<maxConnections>25</maxConnections>
<connectionTimeout>1.0</connectionTimeout>
</defaultProvider>
</database>
7. After the installation login to the server admin console with the admin username and password which is admin admin in our case

8. Review the server settings etc from the admin web console

9. Incase the server setup did not go as planned we can reinstall the server again by dropping the database , creating a fresh empty database and modifying the following from true to false in openfire.xml file in location /opt/openfire/conf
<setup>true</setup>
Test the XMPP Server Installation using Spark client
1.Spark can also be downloaded from the same url as was used to download server . Choose your operating system for download
2.Register a spark client with the server

3. after registering the client presence should be indicated in the user summary by online status
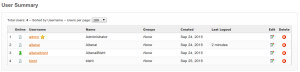
4.Register another client with the same conf except username and password and perform messaging between them

XMPP Java Client
Source Code for a Simple Java Application using Smack4 communicating with XMPP servers
package testxmppsmack;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.jivesoftware.smack.ConnectionConfiguration.SecurityMode;
import org.jivesoftware.smack.SmackException;
import org.jivesoftware.smack.XMPPException;
import org.jivesoftware.smack.SmackException.NotConnectedException;
import org.jivesoftware.smack.chat.Chat;
import org.jivesoftware.smack.chat.ChatManager;
import org.jivesoftware.smack.chat.ChatMessageListener;
import org.jivesoftware.smack.packet.Message;
import org.jivesoftware.smack.tcp.XMPPTCPConnection;
import org.jivesoftware.smack.tcp.XMPPTCPConnectionConfiguration;
public class JabberSmackAPI {
public static void main(String argsp[]){
XMPPTCPConnectionConfiguration config = XMPPTCPConnectionConfiguration.builder()
.setServiceName("machine")
.setUsernameAndPassword("admin", "admin")
.setCompressionEnabled(false)
.setHost("127.0.0.1")
.setPort(5222)
.setSecurityMode(SecurityMode.disabled)
/* .setSecurityMode(SecurityMode.required) keep this commented */
.setSendPresence(true)
.build();
// Create a connection to the the local XMPP server as defined in config above.
XMPPTCPConnection con = new XMPPTCPConnection(config);
// Connect to the server code is encapsulated in try/catch block for exception handling
try {
con.connect();
System.out.println("Connected "+con.isConnected());
} catch (SmackException | IOException | XMPPException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
//Login before performing other tasks like messaging etc
try {
con.login("altanai", "aaa");
System.out.println("Loggedin "+con.isAuthenticated());
} catch (XMPPException | SmackException | IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Start a new conversation with another account holder caled altanaibisht ( I created 2 user accounts one with my first name and another with fullname)
Chat chat = ChatManager.getInstanceFor(con).createChat("altanaibisht@localhost");
try {
chat.sendMessage("Did you try out the new code i send you last night ?");
System.out.println("Chat Send ");
} catch (NotConnectedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Disconnect from the server
con.disconnect();
}
}
Some errors and their resolution while building and running the above code as Java Application are as follows :
1. Cannot instantiate XMPPConnection
Use XMPPTCPConnection instead of XMPPConnection in Smack 4.
2. Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.xmlpull.v1.XmlPullParserFactory
need to have XPP3 (XML Pull Parser 3) in your classpath. Smack 4 does no longer bundle it (unlike Smack 3).
Download the xpp3 from http://www.extreme.indiana.edu/dist/java-repository/xpp3/distributions/
3. Exception in thread “main” java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: de/measite/minidns/DNSCache
http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/de.measite.minidns/minidns/0.1.3
4. For the jxmpp-util-cache-0.5.0-alpha2.jar
Install it from http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.jxmpp/jxmpp-util-cache/0.5.0-alpha2
5.Exception in thread “main” java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/jxmpp/util/XmppStringUtils
http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.jxmpp/jxmpp-core/0.4.1
6. Exception in thread “main” java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/http/conn/ssl/StrictHostnameVerifier
http://www.java2s.com/Code/Jar/a/Downloadapachehttpcomponentshttpclientjar.htm
7.Exception in thread “main” java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/xbill/DNS/Lookup
http://www.java2s.com/Code/Jar/d/Downloaddnsjava211jar.htm
8.org.jivesoftware.smack.SmackException$ConnectionException: The following addresses failed: ‘machine:5222’ failed because java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused
.setHost(“127.0.0.1”)
.setPort(5222)
9. org.jivesoftware.smack.SmackException: javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target
.setSecurityMode(SecurityMode.disabled)
Once the program build and runs succesfully connecting to the XMPP server ( which is running ofcourse ) , open a sapark client and test the application with it.

Summary
An alternative to XMPP messaging is the SIP for Instant Messaging and Presence Leveraging Extensions (SIMPLE) based on Session Initiation Protocol (SIP).
References :
1.XMPP.org
https://xmpp.org/
2.Getting started from Igniterealtime.org
https://www.igniterealtime.org/builds/smack/docs/latest/documentation/gettingstarted.html
3.IETF RFCs on XMPP ( 2004 ) –
RFC 3920 http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3920.txt
RFC 3921 http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3921.txt
4. Extensions on XMPP
http://xmpp.org/xmpp-protocols/xmpp-extensions/
5. XMPP API explanation by grepcode
http://grepcode.com/file/repo1.maven.org/maven2/org.igniterealtime.smack/smack-core/4.0.0-rc1/org/jivesoftware/smack/XMPPConnection.java