- IP communication
- ROI
- Third party interaction
- VAS
- VOIP
- Hosting the PBX
- Convergence Vision
- Fixed Mobile Convergence (FMC)
- Unified Communication(UC)
- Bring your own device (BYOD
- IMS provided Network Interoperability and Access Independence
- Intelligent Network —> Next Generation IMS System
- Circuit Switched Voice –> Packet based VOIP
There has been rapid evolution of telecom platform over the last few decades. Starting from the the mobile phone network-enabled universal communication agnostic to actual location to present day high bandwidth high data rate entertainment/ streaming like applications. The affordable, personal communication system has converged to enterperise level secure communication systems that cater to low latency and highly secure end to end encrypted scenarios.
IP communication
Some of the positive aspects of using IP communication over traditional communication systems are :
Higher ROI( Return of investment)
ROI is a big factor for SME before making the switch to IP telephony inplace of traditional established system like landline phone and cables. However it is for a fact that once the VOIP comm system is setup , it most certainly reduces call costs by 70%.
Third party Interations
It is often a necessaity to integrate communication system with CRM (content realationship management ) systems or Sales management systems or other lead gtracking systesm which are driven from communications with possible clients or investors ( called leads). Since most web portals are on IP protocl as HTTP, VOIP fits very well, with the click to call on webpage itself among other features such as directory integration , notofoication , call scripts etc.
VAS ( Value Added Service)
Value Added Services , refer to services build on top of existing underlying mobile communication call and sms. These could be innovation usecases build using -IVR / DTMF such as cricket score, astrology updates or call recoring , find-me-follow-me applicatoion for multiple devices , voicemail/ visual voice mail , re-routing to home phone or assiatnt phone, called ID etc. In short it can add intelligence to the way calls are managed .
As bandwidth has increased, so has the proliferation of VoIP systems. From the user’s perspective, modern mobile devices deliver the converged, multi-media communication and entertainment experience.
VOIP
VOIP , short for Voice over IP , is called so beacuse it not only converts your voice calls in analog voice into digital packets but also channels voice data through IP networks such as LAN , WAN , Internet etc using the Internet Protocol (IP) .
- VOIP system on LAN ( Local Area Network ) can use it as its backbone system to establish communication between endpoints . For example : Office communication system within the same enterprise/building.
- Similarity VOIP over WAN ( Wide Area Network ) use the help of IP PBX and VoIP service provider to enable communication across Internet . For example : OTT providers and internet calls.
- By using the services of telecom providers in support with above plan it is also possible to land a VOIP call onto a real phone over GSM / PSTN via gateways.
For a provider of IP telephony system, number of factors come into picture such as :
- Bandwidth : Low bandwidth has always been a big concern for IP calls especially due to packet loss and thus high noise. While a LAN connection ensures good experience, calls over internet or VOIP PBX are not necessarily as neat. Network switching between different Internet service providers causes congestion and lags too.
- Inter-operability : Connecting remote works / employees to the VOIP network requires interoperablity between their hand held device like android , ios , tablets , smart watch or other types od communication devices such as hardphone, desktop-systems , kiosk , surveillance cams etc is a challenging considering the underlying OS and networking support.
- Traffic: Maximum simultaneous call or peak traffic rate can create bottlenecks in communication channel or worse still result in high bandwidth usage. For example as p2p conf call between 5 parties will create a mesh network between each participant resulting in 4 outgoing and 4 incoming channels.
- QoS (Quality of service ) :
- Call drops ,
- prioritization of important calls ,
- Security preventing the attacks and hacks ,
- keeping information secure by encryption end to end
- AAA : managing Authentication, Authorization and accounting
- Reuse existing Hardware :
- Replacing old hardware or installing softphone apps on mobiles etc .
- Reuse old servers . Manage setup between datacentres and cloud deployments
- Administravtive hurdles between different counteries and geographies for using hardware
- Scaling
- How quickly can it scale up or scale down ?
- Will the communication system grow horizontly or vertically ?
- How to ensure that the growing system can accommodate new users , physical office location , remote centers , call centres etc ?
- Codecs : Under low bandwidth condition it is a good idea to switch to low resolution ( in case of video ) and low bandwidth codec ( in case of audio ) .
Other factors such as privacy , accounability , Lawful interception ( legal requirnments in many enterprises ) , Auditing , SLA ( Service Level Agreements) to ensure the system is up 99.99 % of time and agrreeing to pay compensation if system is down for longer duration than 0.01 % of time so on.
Hosting the PBX
Unified communication Solutions as SaaS or IaaS refer to on-premise or cloud-hosted IP PBX Solutions. Comparison of both is as follows
| On -premise | Cloud Based |
| The solution is usually of the SaaS nature ( software as a service ) which is hosted by the consumer / business unit itself . | The service provider offers his infrastructure to the consumer as a service and bills monthly / yearly etc . |
| Hosting the solution system on premise and setting up the infrastructure means more customization and flexibility but it also means more investment and maintenance . | On the other hand hosting the solution on cloud is often a quick setup with relatively lower upfront payment. The billing is either carried out per per user basis or based on consumption . The data is synced to cloud servers for storage and can be fetched from there when required such as cloud synced Call-logs or contact-book . |
Convergence Vision
We already know some of the latest trends of industry with respect to telecom convergence such as :
FMC
Fixed Mobile Convergence (FMC) stands for integrating user’s fixed desk phone with his mobile phone. Call continuity is a VAS( Value added service ) which lets him to switch calls between different call devices even softphones , mid call also. It has multi-faced advantages such as not missing any call on account of being out of office , having the same call preferences on each device such as blocked numbers , IVR settings etc .
UC
Unified Communication(UC) refers to the accessibility of all communication and collaboration services from the users call agent ( phone / soft-phone ) . These services can include file transfer , chat , conference , call settings , blocking , white-listing , fax , cloud sync , call logs , called ID , favorites , recording .
Read more about Unified communication and collaboration here .
BYOD
Bring your own device (BYOD) is one of the hottest trends in industry almost across all domains where user is expected or is given to option to bring his personal laptop for official use . It is the responsibility of enterprise comm system to seamlessly integrate it with in-office communication system and provide the same privileges and security to business critical applications as preset in configuration settings . It increases the flexibility and productivity while keeping the infrastructure cost down.
IMS provided Network Interoperability and Access Independence
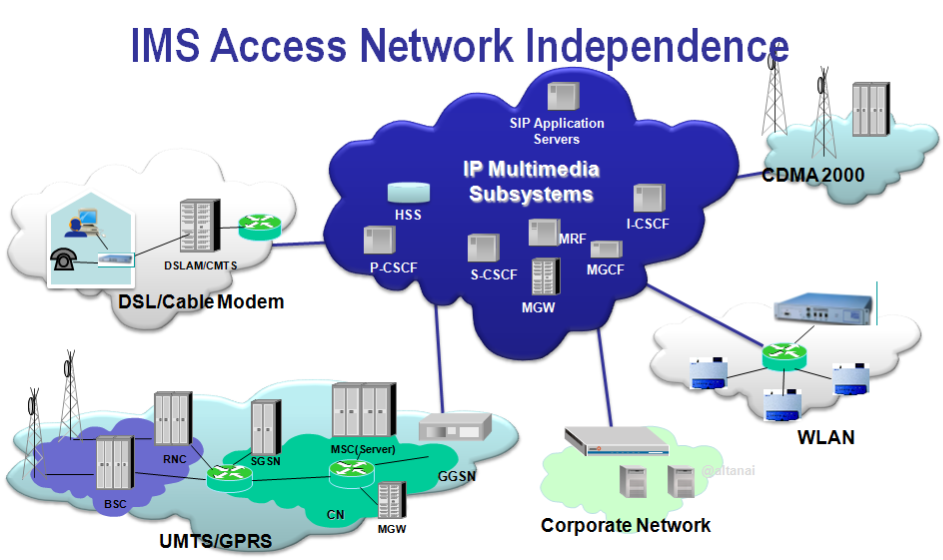
IMS based tele-coommunication convergence described in figure below
- clients get direct connectivity to IP PBX in offices or hotels
- home users connect through cable wires or Wifi/WiMax
- non SIP based legacy endpoints connect via signalling and media gateways
The access endpoints connecte to a single managed core IP network which intercoonectes with IMS core . The back end system not only manages calls and sessions but also registration , billing , operations and adminstartion.
Intelligent Network —> Next Generation IMS System
The signalling protocols migration like from signalling system 7 (SS7) to session initial protocol (SIP) have been taking place in Telco-Industry. Similarly nodes of legacy network like signal transfer point (STP) of legacy network are being migrated to call session control function (CSCF) of IMS that allows the rapid development and deployment of enhanced, revenue-generating multimedia services for fixed, mobile and cable operators.
IMS architecture enables operators to seamlessly run a plethora of next-generation converged services over their fixed, mobile and cable networks, achieve a faster time-to-market for new services and have fewer performance bottlenecks.

Business benefits of IMS
- Delivering Services: Delivering services and applications on a “wherever, however, whenever” basis.
- Multimedia services: Enabling service providers to offer multimedia services across both next-gen, packet-switched networks and traditional circuit-switched networks.
- Protocol stack: IMS architecture provides pipes and protocols onto which service providers can attach no. of applications very conveniently.
- Open Source standard: IMS architecture is based on open standard which makes it possible for different vendors of hardware and software to integrate with each other seamlessly.
As a subscriber, one of the main benefits of the IMS architecture is the capacity of the network to deliver the same set of services whatever the access network used.
This is made possible thanks to the centralization of the service execution process. A specific call server of the control plan (called Serving Call Session Control Function, S-CSCF) is responsible for invoking the application servers based on criteria provisioned in the central database. The S-CSCF gets these criteria (called Initial Filter Criteria) during the user’s registration in the IMS network.
Circuit Switched Voice –> Packet based VOIP
Voice over IP revolutionized in the Telecommunication space.It also makes your communication experience much richer and nicer with a series of enhanced features and extended possibilities. The no. of user migrating from traditional circuit switched network to IP has been quite substantial in recent years. CSP are embracing VOIP technology as a potential revenue generator and investing huge chunk of money to create value propositions for themselves in VOIP.
In conclusion here are the top business benefits of adopting a converged and unified IP telephony solution such as IMS and SIP are
- Cost Savings : Saving money is the number-one reason most businesses and households make the switch to a VoIP system, VoIP systems don’t require a phone cabinet or on-site routing equipment- just phones.
- Features: VoIP also allows users to take advantage of advanced features only available on internet-based phone systems. Features like online call monitoring, and online phone system access to add or configure extensions are also available with VoIP systems.
- Flexibility: VoIP allows people to go mobile and call directly from their cell phone and be charged at low VoIP rates
- Tracking Options: Since VoIP is an internet-based system, user can track and manage their system from their computer. Most VoIP systems allow user to track call volume and call time fairly easily- a feature that can be especially helpful for businesses that bill clients hourly or for time spent on the phone.



