- Traditional trunk call
- SIP trunk (older) systems
- Centralized SIP Trunk Model
- SIP trunking is an IP-based alternative to ISDN trunking services
- Planning to set up SIP trunk
- Features of SIP trunking
- Future of SIP trunks
With the dawn of IP telephony service and cloud communication platforms in recent years, the SIP has caught the attention of many application developers. while SIP is essentially a session management multimedia signalling protocol its generic stack can be used for various use cases from IoT camera streaming sessions to call centres even auto calling for purpose of sharing OTP(one-time password) etc. In this I will highlight the usecase of large calltraffic and the use of SIP trunks.
SIP based trunking can provide significant cost savings and business process improvements by supporting the native SIP protocol that controls the VoIP systems used in call centres and business communication platforms.
- (+) unified communication
- (+) lower telco network
- (+) streamline operations for multicountry/ geography
Traditional trunk call
In the past, telephone systems used trunk lines to connect different parts of the network. Trunk lines were long-distance communication lines that connected telephone exchanges in different locations. Trunk calls were calls made over these trunk lines. They were typically used for long-distance communication, as they allowed calls to be made between exchanges that were geographically far apart. Trunk calls were generally more expensive than local calls, as they involved the use of long-distance communication lines.

Traditional trunk calls operated like a circuit with local loops , trunk lines and switching offices. The telco acted as carriers that sell of lease communication lines to facilitate communication over long distances using local exchanges and interexchange carriers.
In the early days of telephone systems, trunk lines were typically made of copper wires or cables. Later, trunk lines were replaced with satellite links and fiber optic cables, which provided higher capacity and faster transmission speeds. Today, with the widespread adoption of VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) technology, many telephone systems no longer use trunk lines in the traditional sense. Instead, they use virtual connections, such as SIP trunks (Session Initiation Protocol trunks), which allow organizations to make and receive phone calls over the internet. SIP trunks are generally more flexible and cost-effective than traditional trunk lines, and do not require the installation of additional hardware.
Voice trunk Lines in SS7 based Next Generations IN networks used media gate ways and MGCP, H323 protocols

SIP trunk (older) systems
SIP is a protocol that is commonly used in VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) systems to set up, modify, and terminate sessions that involve the exchange of audio, video, and other media. SIP Trunks are virtual voice channels (or paths) which deliver media (voice, video, IM) over an IP network to a designated endpoint. SIP Trunks can be thought of as a virtual line or concurrent call path. SIP Trunks are delivered over an IP connection like Tier One Carrier or Voice Optimized Recommended or UDP. SIP Trunk may be over-subscribed ie can have more numbers than trunks for example G.711 – 17 calls over T1 or G.729a – 45 calls over T1. SIP Trunking can be provided as one-way or two-way lines. Direct Inward Dialing (DIDs) can be used for toll-free number service.
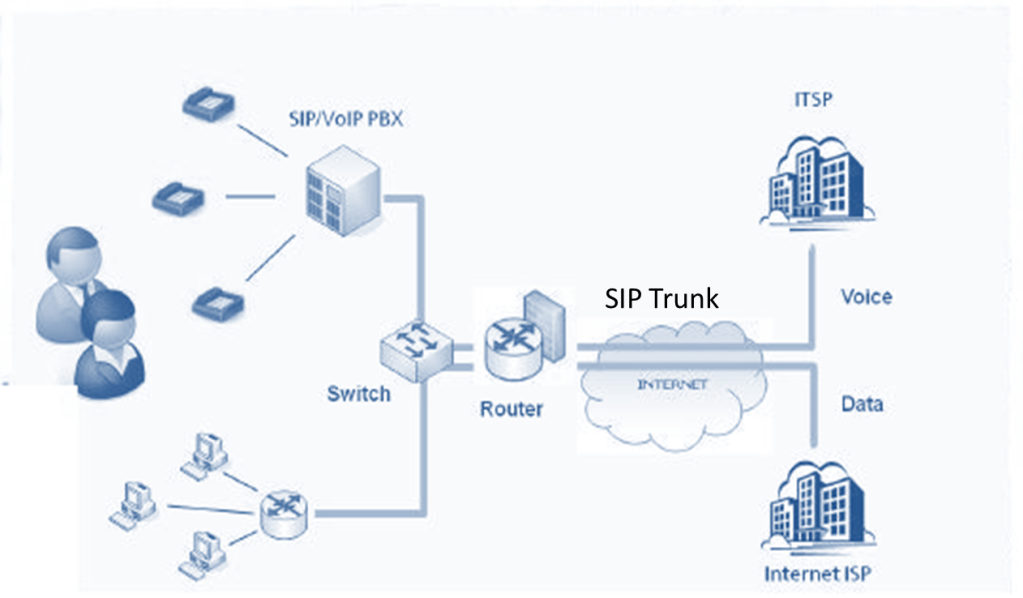
Centralized SIP Trunk Model
Centralized SIP Trunk Model is designed to aggregate all calls from all sites and funnels them into a single entry point. Each site has its own SIP trunk termination of the appropriate capacity for calls to and from that site.

Such SIP trunks models offer benefits in three significant areas:
- Cost savings, arising from many factors including reduced telecommunications network charges and streamlined operations.
- Unified communications, where voice, video, email, text and other messaging technologies are combined to provide greater flexibility for users by enabling new ways to transfer information and manage connectivity. Many SIP trunk providers offer advanced features such as call forwarding, call waiting, and voicemail, which can improve the overall communication experience for employees.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery, where the right physical configuration in conjunction with intelligence in the network can be leveraged to provide uninterrupted communications and alternative means to stay connected for employees in the event of system bottlenecks or failures.
SIP trunking is an IP-based alternative to ISDN trunking services
SIP Trunking is a low-cost IP-based alternative to ISDN offering for medium to large businesses needing upwards of several tens of channels in a trunk, often across multiple sites, with IP VPN access.
- (+) Optimal utilization of bandwidth by delivering both data and voice in the same bandwidth
A telephony company such as a telecom service provider may expose SIP trunks as a means of connecting inbound or outbound calls through its telecom network. For the integrator ( or the service provider managing the other enedpoint of the call leg ) it can be no different that a traditional phone call.The SIP signalling however is useful for enabling better session understaning using standard SIP requests and responses as compared to SS7 or PRI lines.
Planning to set up SIP trunk
•Cost analysis
•Assess traffic volumes and patterns
•Assess network design implications
•Emergency call policy
•Define production user community phases
•Define user community to pilot
•Evaluate future new services
•Assess security precautions
The steps to set up a SIP trunk connection may vary depending on the specific provider and the equipment being used. However, here are some general steps that are often involved in the process:
- Choose a SIP trunk provider: Research and compare different SIP trunk providers to find one that meets your organization’s needs and budget.
- Sign up for a SIP trunk account: Follow the provider’s instructions to sign up for a SIP trunk account. This may involve completing an online form, providing contact information and payment details, and selecting the desired features and services.
- Configure your VoIP phone system: Consult your VoIP phone system’s documentation to learn how to configure it to work with a SIP trunk. This may involve specifying the SIP trunk’s IP address and port number, as well as any authentication credentials that are required.
- Test the connection: Once the SIP trunk is set up, it is a good idea to test the connection to ensure that it is working properly. Make a few test calls to verify that the connection is functioning as expected.
- Use the SIP trunk: Once the SIP trunk is set up and tested, it can be used to make and receive calls using your VoIP phone system.
SIP Trunking platform has to integrate with multiple networks seamlessly. Components for setting up a SIP trunking system requires atleast these
- Compliance with standrad signalling protol, like SIP.
- SBC( Session Border Controller ) facing the private PBX
- Gateway for specific endpoints such as PSTN gateway , public internet gateway etc
- L3/L4 Layer switches
- Telco operator lines
- Codec support
Kamailio is an open-source SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) server that can be used to create a SIP trunk. Kamailio can be PBX used to connect different locations within an organization, enabling employees to communicate with each other using their VoIP phones. Kamailio can also be used to set up a SIP trunk in a number of ways. For example, it can be used to connect an organization’s VoIP phone system to the public telephone network, allowing employees to make and receive calls from outside the organization.

Kamailio is a highly flexible and customizable SIP server that can be configured to meet the specific needs of an organization. It offers a range of features and functionality, including call routing, load balancing, and security. Kamailio is a popular choice for organizations that want to set up a SIP trunk because it is open-source and can be customized to meet their specific needs.
Features of SIP trunking
SIP trunk with VoIP phone systems are often preferred over traditional phone systems because they are generally more flexible and cost-effective. They allow employees to make and receive calls from any device with an internet connection, including desk phones, smartphones, and laptops. They can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing communication needs and do not require the installation of additional physical hardware. Some factors to consider when evaluating SIP trunks include:
- Cost: It is important to compare the costs of different SIP trunk providers and consider factors such as monthly fees, per-minute charges, and any additional fees for features or services.
- Coverage: Make sure that the SIP trunk provider has coverage in the areas where your organization needs to make and receive calls.
- Quality: The quality of a SIP trunk can vary greatly depending on the provider and the connection. Be sure to research the provider’s reputation for call quality and reliability.
- Features: Different SIP trunk providers may offer different features, such as call forwarding, call waiting, and voicemail. Consider which features are important to your organization and make sure that the SIP trunk provider offers them.
- Customer support: It is important to choose a SIP trunk provider that offers reliable customer support in case you experience any issues with your service.
Other features that are good to have is integration to existing backend for OSS/BSS stack. Some of the feature set for a carrier grade SIP trunking solution are listed here
- Inbound and outbound trunks
- Number Import/Export
- Security
- Dynamic registeration of users
- Authentication and Authorization
- Security (SRTP)
- Cost Savings
- Low cost for large traffic volumes instead of charges of call per second
- CDR for tracing and monitoring call failures
- Clear media stream ( no robotic or choopy audio). Good MOS score
- realtime traffic monitoring to rule out bad players.
- Inbound and Outbound call – Call Establishment, Rejection, Termination
- DDI: Direct Dialling-In ranges can be provided on the SIP Trunk
- CLIP(Calling Line Identification Presentation )/CLIR Calling Line Identification Presentation Restriction) for Inbound and Outbound
- Call Management
- AUTH Code Screening
- Combined Screening
- Data Call Screening
- Local Screening
- Anonymous Call Rejection: Anonymous Call Rejection
- Incoming Call Barring: bar receiving of calls to certain extensions
- Outgoing Call Barring: Restrict calls to certain numbers
- Incoming Call Diversion – unconditional, busy, and unreachable
- Call Admission Control: Call Admission Control (CAC) is a mechanism to restrict the number of simultaneous sessions (calls)
- Incoming Call Diversion (DestNo not reachable, CAC exceeded, unconditional)
- Geographic and Non-Geographic Number Support
- Multiple Codec Support
- Emergency Calling: Emergency Calls are routed on a priority basis irrespective of the customer’s available channel
Trunking inbound services voice can be used to support contact centres, conferencing, number translation services etc. Regulatory requirements for the operation of the customer in the PSTN of respective countries must be met with Country Specific Emergency Calling support Enhanced feature set for SIP trunking should include the features of the SIP Trunking with Multicountry support
- Enhanced CAC(Call Admission Control) – Directional & Network
- Global Dial Plan Support
- Proactive MCID (Malicious CallerId) Identification and tracing
- Call Distribution(CD)
- Intelligent Routing involving machine learning and constant feedback
- Origin Based Routing
- Menu Routing
- Origin Dependent Routing (ODR)
- PIN Routing
- Dynamic Route Select
- Time-Dependent Routing (TDR)
- Uniform Load Distribution(ULD)
- International Routing
- Mobile Routing
- Payphone Routing
- Product Association
Ultimately, the most useful SIP trunk for your organization will depend on your specific needs and budget. It is a good idea to research and compare different SIP trunk providers to find the one that best meets your organization’s needs.
Future of SIP trunks
SIP trunking systems are likely to continue to be an important part of the telecommunications landscape in the future. As more and more organizations adopt WebRTC or SRT based VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) technology for their phone systems, the demand for SIP trunks is likely to continue to grow. One trend that is expected to shape the future of SIP trunking is the increasing adoption of cloud-based communication systems. As more organizations move their communication systems to the cloud, they are likely to turn to SIP trunks as a way to connect their phone systems to the public telephone network and enable remote communication. Another trend that is expected to impact the future of SIP trunking is the increasing adoption of 5G technology. 5G networks offer faster speeds and lower latency, which may make it possible to use SIP trunks for real-time communication applications such as interactive and/or immersive video conferencing.
