PJSIP is a robust, open-source SIP stack written in C and distributed under the GPL license. It provides a comprehensive framework for building SIP-based VoIP applications, WebRTC clients, and multimedia communication systems. PJSIP’s modular architecture, high performance, and extensive codec support make it an ideal choice for embedded systems, mobile applications, and enterprise communication platforms.
- Architecture Overview
- Media Negotiation: SDP Offer/Answer
- Installation & Build
- Key Takeaways
- References
Architecture Overview

SIP stack written in C. Available under GPL. PJSIP is built on a layered architecture consisting of three primary components:
User Agent (UA)
The User Agent module manages SIP endpoints and their lifecycle.
Key Attributes:
local_infowith taglocal_contactcall_id
Core Operations:
pj_status_t pjsip_ua_init(endpt, param); // Initialize the UApj_status_t pjsip_ua_destroy(void); // Shutdown the UApjsip_module* pjsip_ua_instance(void); // Get UA module instancepjsip_endpoint* pjsip_ua_get_endpt(ua); // Get the SIP endpointDialog Management
Dialogs represent the relationship between two endpoints and maintain the state of SIP communications.
Key Attributes:
state– Current dialog statesession_counter– Active session countinitial_cseq,local_cseq,remote_cseq– Sequence numbersroute_set– Route headers from responseslocal_info/local_contact– Local endpoint informationremote_info/remote_contact– Remote endpoint information
Core Operations:
// Dialog creationpj_status_t pjsip_dlg_create_uac(ua, local_uri, contact, …);pj_status_t pjsip_dlg_create_uas(ua, rdata, contact, &dlg);pj_status_t pjsip_dlg_fork(old_dlg, rdata, &dlg);// Dialog configurationpj_status_t pjsip_dlg_set_route_set(dlg, route_set);pj_status_t pjsip_dlg_inc_session(dlg);pj_status_t pjsip_dlg_dec_session(dlg);pj_status_t pjsip_dlg_add_usage(dlg, mod);// Request/Response handlingpj_status_t pjsip_dlg_create_request(dlg, method, cseq, &tdata);pj_status_t pjsip_dlg_send_request(dlg, tdata, &tsx);pj_status_t pjsip_dlg_create_response(dlg, rdata, code, txt, &tdata);pj_status_t pjsip_dlg_modify_response(dlg, tdata, code, txt);pj_status_t pjsip_dlg_send_response(dlg, tsx, tdata);pj_status_t pjsip_dlg_send_msg(dlg, tdata);// Dialog association helperspjsip_dialog* pjsip_tsx_get_dlg(tsx);pjsip_dialog* pjsip_rdata_get_dlg(rdata);Module Framework
Modules are pluggable components that handle specific SIP functionality.
Key Attributes:
name– Module identifierid– Unique module IDpriority– Execution order
Callbacks:
pj_bool_t on_rx_request(rdata); // Incoming request handlerpj_bool_t on_rx_response(rdata); // Incoming response handlervoid on_tsx_state(tsx, event); // Transaction state change handlerSDP state Offer/ Answer transition

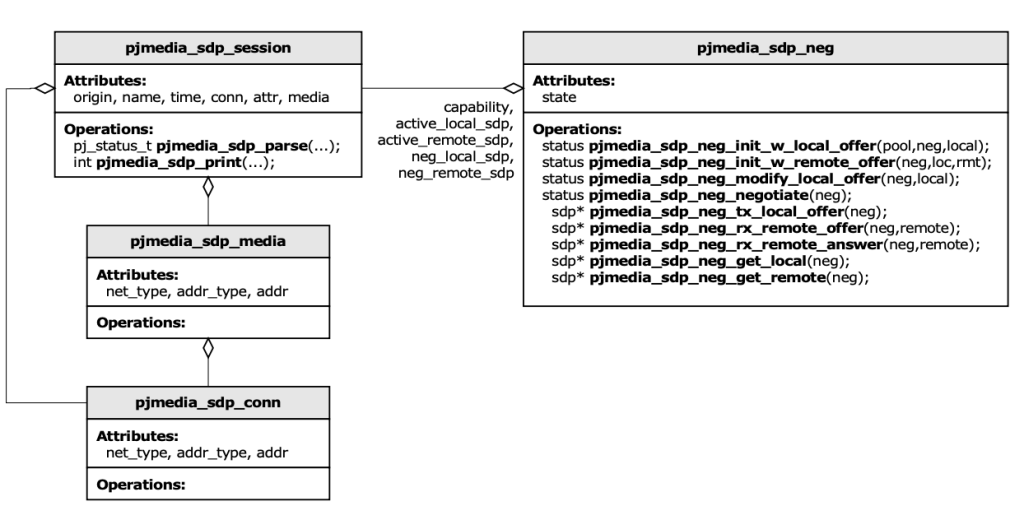
Media Negotiation: SDP Offer/Answer
PJSIP implements the SDP Offer/Answer model for media negotiation. The negotiator manages state transitions and ensures compatible media codec selection between endpoints. This crucial component ensures both parties agree on compatible audio/video codecs before establishing media streams.
Installation & Build
Prerequisites
Required:
- GNU make (other make tools incompatible with PJSIP build system)
- GNU binutils for target platform
- GNU gcc for target platform
Optional Libraries:
- ALSA – Audio support on Linux systems
- OpenSSL – TLS/DTLS encryption support
- Video Support – Video4Linux2 (v4l2), FFmpeg, libx264, libvpx, OpenH264
Quick Start Guide
Step 1: Download and Extract
wget https://www.pjsip.org/release/2.9/pjproject-2.9.tar.bz2tar -xvjf pjproject-2.9.tar.bz2cd pjproject-2.9Step 2: Configure with Required Features
./configure --enable-shared --disable-static --enable-memalign-hack --enable-gpl --enable-libx264Watch for successful feature detection:
checking opus/opus.h usability... yeschecking for opus_repacketizer_get_size in -lopus... yesOPUS library found, OPUS support enabledStep 3: Build and Install
make depmakemake installKey Configuration Options
| Option | Purpose |
|---|---|
--enable-shared | Build shared libraries |
--disable-static | Don’t build static libraries |
--enable-gpl | Enable GPL-licensed features |
--enable-memalign-hack | Fix memory alignment issues |
--disable-sound | Exclude sound device support |
--disable-video | Disable video features |
--with-openssl=DIR | Specify OpenSSL location |
--with-opus=DIR | Specify OPUS codec path |
--with-ffmpeg=DIR | Specify FFmpeg location |
Program
create library instance and initiate with default config and logging
lib = pj.Lib() lib.init(log_cfg = pj.LogConfig(level=LOG_LEVEL, callback=log_cb))
create UDP transport listening on any available port
transport = lib.create_transport(pj.TransportType.UDP,
pj.TransportConfig(0))
create sipuri and local account
my_sip_uri = "sip:" + transport.info().host + ":" + str(transport.info().port)
acc = lib.create_account_for_transport(transport, cb=MyAccountCallback())
Function to make call
def make_call(uri):
try:
print "Making call to", uri
return acc.make_call(uri, cb=MyCallCallback())
except pj.Error, e:
print "Exception: " + str(e)
return None
Ask user input for destination URI and Call
print "Enter destination URI to call: ",
input = sys.stdin.readline().rstrip("\r\n")
if input == "":
continue
lck = lib.auto_lock()
current_call = make_call(input)
del lck
shutdown the library
transport = None acc.delete() acc = None lib.destroy() lib = None
Run
➜ ~ python simplecall.py sip:altanai@127.0.0.1 09:58:09.571 os_core_unix.c !pjlib 2.9 for POSIX initialized 09:58:09.573 sip_endpoint.c .Creating endpoint instance… 09:58:09.574 pjlib .select() I/O Queue created (0x7fcfe00590d8) 09:58:09.574 sip_endpoint.c .Module "mod-msg-print" registered 09:58:09.574 sip_transport.c .Transport manager created. 09:58:09.575 pjsua_core.c .PJSUA state changed: NULL --> CREATED 09:58:10.073 pjsua_core.c .pjsua version 2.9 for Darwin-18.7/x86_64 initialized Call is CALLING last code = 0 ()

Debug Help
Isssue1 Undefined symbols for architecture x86_64:
“_pjmedia_codec_opencore_amrnb_deinit”, referenced from:
_amr_encode_decode in mips_test.o
_create_stream_amr in mips_test.o
“_pjmedia_codec_opencore_amrnb_init”, referenced from:
_amr_encode_decode in mips_test.o
_create_stream_amr in mips_test.o
ld: symbol(s) not found for architecture x86_64
clang: error: linker command failed with exit code 1 (use -v to see invocation)
make[2]: *** [../bin/pjmedia-test-x86_64-apple-darwin18.7.0] Error 1
make[1]: *** [pjmedia-test-x86_64-apple-darwin18.7.0] Error 2
make: *** [all] Error 1
Root Cause: macOS has strict architecture compatibility requirements. This typically occurs when building for OpenCORE AMR codec support that isn’t properly linked
./configure --enable-shared --disable-static --enable-memalign-hack
make dep
make install
cd pjproject-2.9/pjsip-apps/src/python/
python setup.py install
Key Takeaways
- Modular Architecture: User Agents, Dialogs, and Modules work together seamlessly for maximum flexibility
- Production Ready: Battle-tested in millions of VoIP deployments worldwide
- Cross-Platform: Runs on Linux, Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android
- Extensive Codec Support: OPUS, SILK, G.711, G.722, and many more
- WebRTC Compatible: Native support for WebRTC applications and data channels
- Media Negotiation: Robust SDP Offer/Answer implementation ensures codec compatibility
- Python Bindings: High-level Python API (PJSUA) for rapid application development
References
- Official PJSIP Project: https://www.pjsip.org
- Developer Guide: https://www.pjsip.org/release/0.5.4/PJSIP-Dev-Guide.pdf
- Trac Repository: https://trac.pjsip.org/repos
- RFC 3261: SIP Protocol Specification – https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3261
- PJSUA API: High-level SIP User Agent API documentation
