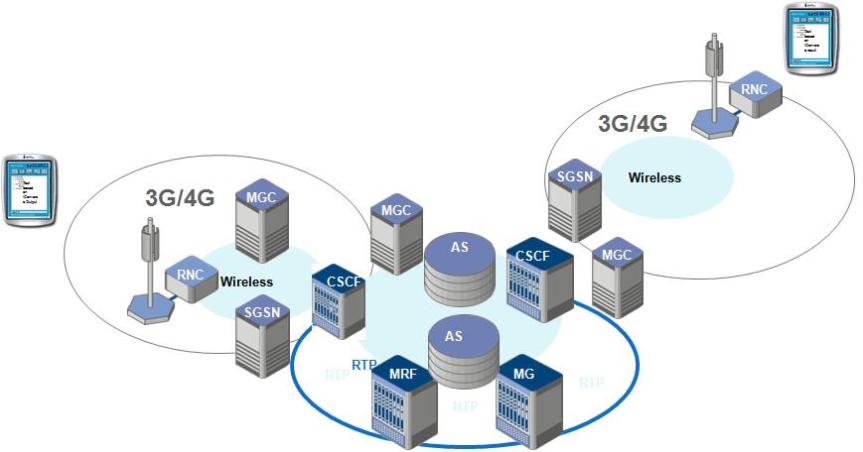
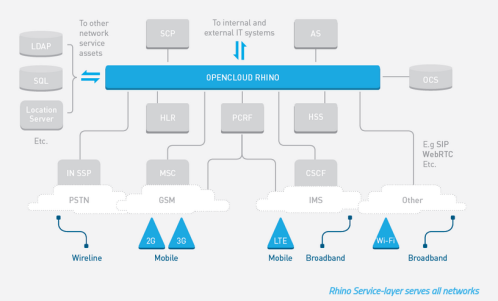
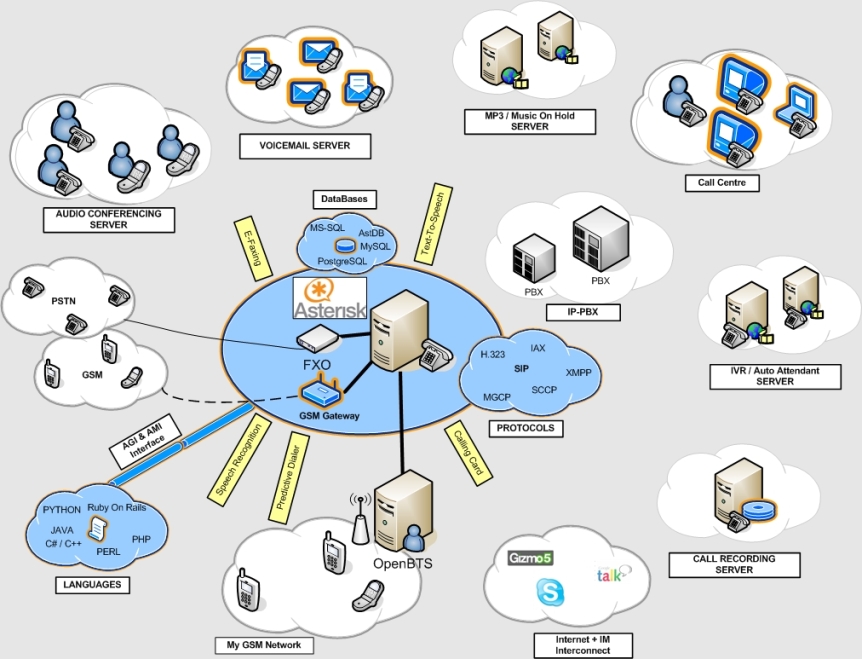
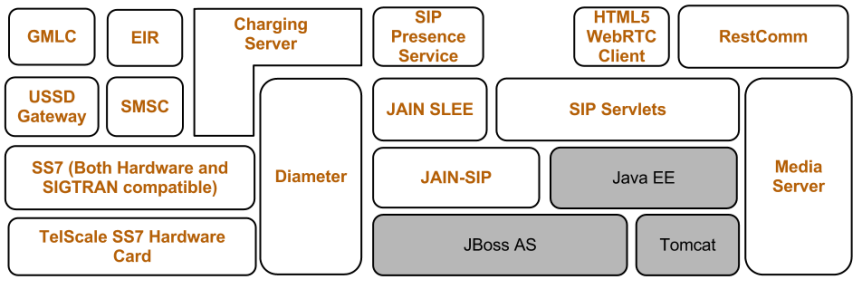
Convergence : Telephone networks and computer networks converging into single digital network using Internet standards.
Components in a Network
- Client computer
- Server computer
- Network interfaces (NICs)
- Connection medium
- Network operating system
- Hub or switch
- Routers- Device used to route packets of data through different networks, ensuring that data sent gets to the correct address
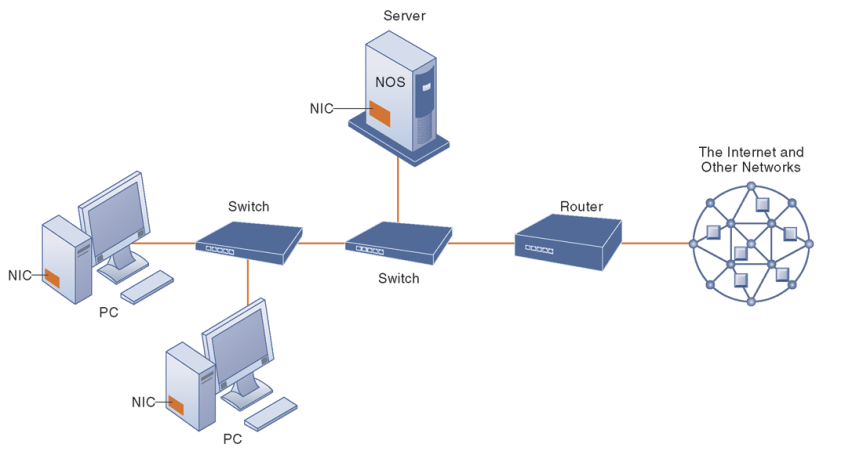
Figure :simple computer network, consisting of computers, a network operating system residing on a dedicated server computer, cable (wiring) connecting the devices, network interface cards (NICs), switches, and a router.
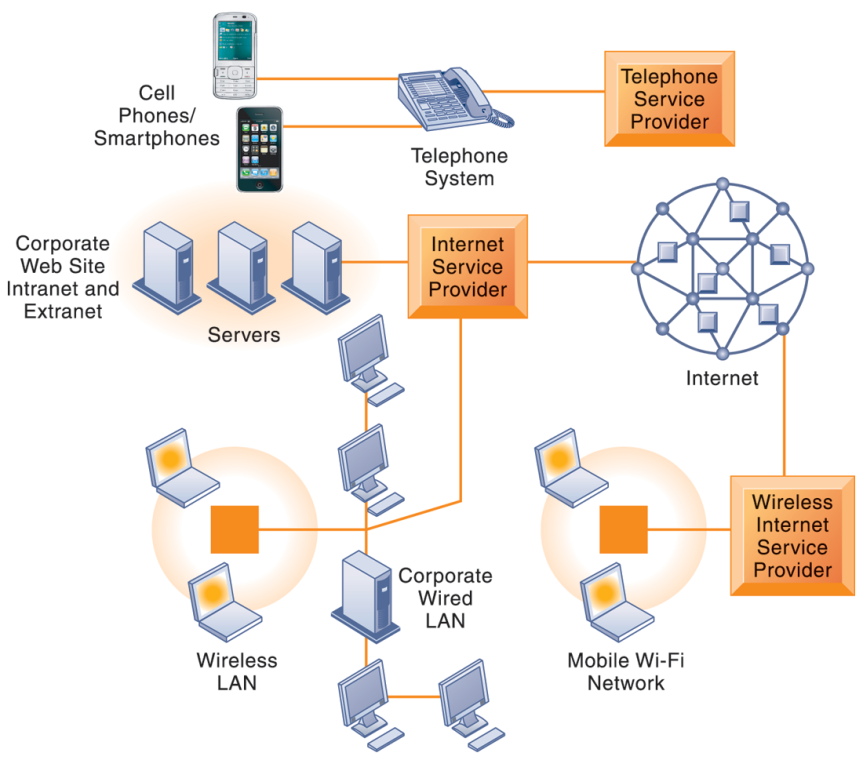
Figure of a Enterprise Network : local area networks (LANs) linked to enterprise level / corporate network . It consists of :
- Powerful servers
- Web site
- Corporate intranet, extranet
- Backend systems
- Mobile wireless LANs (Wi-Fi networks)
- Videoconferencing system
- Telephone network
- Wireless cell phones etc
The convergence of Internet and Telephony opens up new revenue streams for the Communication Service Providers by delivering new innovation based convergent applications.
Before discussing digitization of Communication and telecom we need to first understand packet switching .
What is Packet switching ?
It is a method of slicing digital messages into packets, sending them along different communication paths as they become available. Then reassembling these received packets at destination. It is a more efficient use of network’s communications capacity.
Previous circuit-switched networks required assembly of complete point-to-point circuit.
What triggered this Technology development?
The Internet, IPTV and Social Media networking is evolving dynamically in the end user space of Communication Service Provider. This opens door for delivering new innovative services to end user through these converged applications.
A SP( Service provider ) has to work with multiple Communication Providers globally and based on the experience with the customers, has to conceptualize and implemented new innovative use cases on open platform to reduce the cost and migrate from legacy to Next Generation Networks.
What does convergence mean to
- Equipment Vendors / EV
- Femto / FMC
- Challenges in System Integration
- Box to Solution Sales
- Services software based
- Enterprises
- Low Capex – Hosted Models
- Enterprise Mobility
- IP Enabled Services
- UC to UC
- Web Integration with Mobility
- Telco
- Enterprise communication will be a big focus Area
- Push to EVs for CAPEX
- Wish to leverage Legacy as well
- Challenges in Vertical Solutions
- Will face challenges by OTT players
What will it do, how and in which situation ?
The underlying technology of Internet Telephony Convergent Platform is JAIN SLEE Framework which is open standard for developing core network based applications. It enables development of network agnostic applications , implemented through resource adapters for deploying same applications over different networks like SIP/IN etc.
JAINSLEE framework provides capability to form new complex services through reusable service building block in much easier way then traditional methods. This reduces cost for launching new services and bundled different services into the new convergent service in network agnostic way.
It also bring benefits in term of reducing the dependency on Vendor proprietary platform and eventually bringing down cost involved and Time to market in launching new service.
picture courtesy : Opencloud.com
What problem does this technology seek to solve?
Today communication service provider are facing vendor locking situation where most of services deployed are platform dependent which requires huge cost of investment for launching new services. Traditional service development platforms are major roadblock for operators to launch new collaborative services which involves both voice and data channels as they are not based on open standards and are tied to the vendor specific technologies. Also in a fast changing technology the operators need to switch their focus on new innovative services through which operator can monetize services and provide the value added experience to their end customers. To enable it we proposed and implemented framework which not only act as the new Internet Telephony convergent platform but also in sync with their future network transformation strategy as it is based on open standards. Through this platform same applications can be targeted to different segment of users with minimal cost impact. Some of the application which we have developed are detailed below.
a) Parental Control is an application through which parents can have control over their children’s Internet video on demand request. Once a child requests for any video, preview of the same(short clip of video) at the same instance is send to parents’ smart phones. Parents can see preview and can decide there and then weather it is adequate for his/her kids or not, and can either allow or deny through his mobile.
b) IPTV/VOD session mobility is a service which allow user to transfer their ongoing voice call/video-on-demand session from their smartphone to desktop/computing device/smart-device and vice-versa seamlessly.
c) Converged application like unified communication platform for trader community take advantage of both voice and data services and help trader community in terms of analytics and decision making process.
What is the specific breakthrough of this technology?
Internet and Telephony are two major drivers in Telecom domain. Hence the concept of convergence of Internet and Telephony is of great interest for the Telcos. Internet telephony, also known as voice-over-IP or IP telephony is the real-time delivery of voice between two or more parties, across networks using the Internet protocols, and the exchange of information required to control this delivery. New innovative use case scenarios have been conceptualized and implemented considering new user behavior changes. These bring in value addition to CSPs in order to bring more revenue streams. Solutions like Secure VOIP bring another dimension of innovation as it provides a secured voice communication over the internet using open source software like Asterisk. This solution helps business reduce their operational communication costs using encrypted standard security algorithms.
pic courtesy : asterisk.com
How does this technology compare with other technologies?
Internet telephony convergent platform has the unique value proposition based on new innovative use case scenarios using multiple underlying technologies. These scenarios are implemented using Open Standards. Though many other vendors’ platform also provides some of the facilities of platform in part and pieces but none of them give complete end to end solutions suits to operators as our Internet Telephony convergent platform provides.
How does it help in achieving the goals?
We consider it as solution which can act as foundation block to build a long term partnership with operators especially in area of services landscape. This solution enables operator to monetize different voice and data convergent services and in sync with the operator’s next generation transformation initiative. The services acts as catalyst to increase the data usage of end-users. Strong business case can be built with these services by operators as they meet the future demands of tech savvy end users. These services not only fill the void between communication service provider and social media/internet/video-on-internet but also take advantage of reach of social media/internet and eventually enable operator to add new revenue stream. These services can also help operator to increase their brand visibility with added advantage of social media and internet application bundled with their core services. Operator can charge it on per application basis or can be just carrier and charge for data usage. Convergent services which involves both the voice and data, enable operator to charge on voice services , data services and application usage. With our rich experience in convergent platform domain we believe we can convert significant opportunities in this space.
Explain your journey of Technology development ?
After seeding of concept of Internet Telephony convergent platform SP should explore partner product Software centric platforms like Open cloud, Oracle, Mobicient etc which offers the capability to deliver convergent applications at a low cost and using the open standards. Standards like JAIN SLEE provide capability for developing and delivering such applications across different type of underlying network.
pic courtesy : Mobicents.com
One can develop the complete solution using such open, standard platforms as a base . The complete solution takes care of the real-network issues and solutions for the same. There were many hurdles and roadblock at first. Adaptation to open standards like JAIN SLEE requires fast ramp up as it is quite complex technology. In a small stipulated time a core team should have developed competency through Partner Training inputs and Brain Storming sessions. To test framework at lab, there would be dependency on many open source software and strategic partner products. There would be many incompatibility issues. Its important that such issues be sorted out by exhaustive explorations of products and by bug fixes .
Benefits expected if this Technology is implemented / commercialized
a) Communication service providers are able to realize appreciable cost saving through Internet Telephony convergent platform Operators deployed in their network. This is so legacy platform were costly and difficult to manage. This platform brings innovative and cost effective way of launching new collaborative services which brings new revenue stream.
b) Improved Time to market
c) Extensible architecture for the service helps in extending the service for multiple markets.
Social Benefits
Unified communications, where voice, video, email, text and other messaging technologies are combined to provide greater flexibility for users by enabling new ways to transfer information and manage connectivity. Integration of collaborative services with the social media platform like Facebook , Linkedin , Twitter etc, increases the connectivity and value experience of end users. Through social media based convergent applications operator can further increase their reach to end users by utilizing underlying the Internet Telephony convergent platform.
My Insights
Based on my personal experience while implementing this technology/platform, I think this solution act as catalyst for enabling the transition from network eccentricity to customer eccentricity. This movement is further supplemented through the reduced dependence on legacy vendors and increased adoption of open standard based platforms. Through the converged application layer for Telcos I envisage a platform which is agnostic to underlying network layer. Unified platform allows carriers, mobile operators, and cable operators to rapidly create, manage, and deliver converged video, voice, and data service bundles across multiple networks and devices. It enhance end user experience and enable Telcos to add new revenue stream by offering value added services to their customer.